INTRODUCTION
FILL IN THE BLANKS
Q.01: Fill in the blanks:
(i) ________ is the study of organisms in relation to their environment. (Environmental biology)
(ii) The study of organisms living in fresh water bodies like rivers, lakes etc. is called _________. (Fresh water biology)
(iii) ________ is the branch of biology which deals with the study of social behaviour and communal life of human beings. (Social biology)
(iv) In the ________ body, only six bio-elements accounts for 99% of the total mass. (Human)
(v) All living things and non-living things are formed of simple units called ______. (Cells)
(vi) Various organs in plants and various organ systems in animals are assembled together to form an _______. (Individual)
(vii) A _______ is a group of organisms of the same species located in the same place at the same time. (Population)
(viii) A _______ is based upon observations. (Hypothesis)
(ix) A hypothesis is a result of deductive reasoning or it can be the consequence of ________ reasoning. (Inductive)
TRUE/FALSE
Q.02: Write whether the statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’ and write the correct statement if it is false.
(i) Penicillin was discovered by Edward Jenner from a fungus Penicillium. (False)
CORRECT: Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Flemming from a fungus Penicillium.
(ii) Many diseases such as polio, whooping cough, measles, mumps etc. can be controlled by antibiotics. (True)
(iii) Exposure to the small pox virus allows the body to develop immunity against cowpox virus. (False)
CORRECT: Exposure to the cow pox virus allows the body to develop immunity against small pox virus.
(iv) AIDS is caused by HIV and it spreads through sexual contacts, blood transfusion, by contaminated syringe or surgical instruments. (True)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.03: Each question has four options. Encircle the correct option:
(i) Which one of the followings is a correct sequence in biological method?
(a) Observations – hypothesis – law – theory
(b) Observation – hypothesis – deduction – testing of deduction
(c) Hypothesis – observations – testing of deduction
(d) Law – theory – deduction – observations
ANSWER: (b) Observation – hypothesis – deduction – testing of deduction
EXPLANATION: Biological method starts with chance observation. Then a hypothesis is made by way of deduction or induction which is tested by experiments.
(ii) Which one of the followings is employed in treatment of cancer?
(a) Antibiotics and vaccination
(b) Radiotherapy and chemotherapy
(c) Chemotherapy and antibodies
(d) All of the above
ANSWER: (b) Chemotherapy and antibodies
EXPLANATION: Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are employed to destroy the cancerous cells in the body.
(iii) Which one of the followings is not a viral disease?
(a) Cow pox
(b) Mumps
(c) Tetanus
(d) Small pox
ANSWER: (c) Tetanus
EXPLANATION: Tetanus is caused by bacteria especially Clostridium tetani.
(iv) Which one of the followings is not related to cloning?
(a) Replacement of the nucleus of zygote by another nucleus of the same organism.
(b) Separation of cells of embryo to form more embryos.
(c) The individuals resulting have similar genetic makeup.
(d) Removal of piece of DNA or gene from the cell, and incorporating another gene or piece of DNA in its place.
ANSWER: (d) Removal of piece of DNA or gene from the cell, and incorporating another gene or piece of DNA in its place.
EXPLANATION: Removal of piece of DNA or gene from the cell, and incorporating another gene or piece of DNA in its place is called genetic engineering or gene editing, which is used to modify the genetic trait of an organism. While, cloning is simply an asexually method of obtaining multiple identical copies of an organism in which the nucleus of the somatic cell of one organism is inserted into the fertilized egg cell of another organism whose nucleus has already been removed. The individual produced is the exact copy of the organism whose nucleus is inserted into the fertilized egg.
Q.04: Short Questions:
(i) What do you mean by hypothesis?
(ii) How does law differ from theory?
(iii) What is deductive reasoning?
(iv) Define vaccination.
(v) Write a short note on cloning.
ANSWER:
(i) What do you mean by hypothesis?
Hypothesis: “Hypothesis is the tentative explanation of the observations.” It is the logical consequence of observations. Hypothesis is tested by experiments.
Example: When plasmodium was found in the blood of several malarial patients, it was hypothesized that: “Plasmodium is the cause of malaria.”
(ii) How does law differ from theory?
| THEORY | SCIENTIFIC LAW |
| A series of hypotheses supported by the results of many tests is called a theory. It is less general than scientific laws. Examples: Cell theory, germ theory of diseases. | Scientific law is a uniform or constant fact of nature. It is, virtually, an irrefutable theory. It is more general than theories & affords answers to even more complex questions. Examples: Hardy-Weinberg law, Mendel’s laws of inheritance. |
(iii) What is deductive reasoning?
Deductive Reasoning: “Deductive reasoning moves from ‘general to specific’. It involves drawing specific conclusion from some general principle/assumptions.” It is a way to formulate a hypothesis.Example: If we accept that ‘all birds have wings’ (premise#1) and that ‘sparrows are birds’ (premise#2), then we conclude that ‘sparrows have wings’.
(iv) Define vaccination.
Vaccination: “Vaccination is the inoculation of weakened or dead microorganism of a disease, or proteins or toxins from the organism, into a healthy person to develop immunity against that disease.” Literally, the word ‘vaccine’ has been derived from Latin word ‘vacca’ meaning ‘cow’. This was first of all used by Edward Jenner in 1795, who inoculated the healthy persons with cow pox lesion to prevent from small pox. Later, Pasteur used this technique against the diseases like anthrax, cholera, rabies.
(v) Write a short note on cloning.
Cloning: “Cloning is a technology for achieving eugenic aims. It is the production of genetically identical copies of an organism or a cell by asexual reproduction.”
Clone: “A cell or an individual and all its asexually produced offspring are called clone.” All members of a clone are genetically identical except when mutation occurs.
Method of Cloning: In cloning, the nucleus from a fertilized egg is removed and a nucleus from a cell of a fully developed individual is inserted in its place. The altered zygote is then implanted in a suitable womb where it completes its development. The new individual formed in this way, is a genetically identical clone of the individual whose nucleus was used.Examples: Generally, no normal animal reproduces naturally by cloning. Several insects and many plants do, in some circumstances, whereas few do so regularly.
EXTENSIVE QUESTIONS
(i) Define the following branches of biology: Molecular Biology, Microbiology, Marine Biology, Biotechnology.
ANSWER:
Molecular Biology: “Molecular biology deals with the study of the structure of organisms, cells and their organelles at molecular level.”
Microbiology: “Microbiology is the branch of biology which deals with the study of microorganisms including Bacteria, Viruses, Protozoa and microscopic algae and fungi etc.”
Marine Biology: “Marine biology is the study of life in seas and oceans. This includes the study of the marine life and the physical and chemical characteristics of the sea, acting as factors for marine life.”Biotechnology: Biotechnology is the branch of biology which deals with the use of living organisms, systems or processes in manufacturing and service industries.
(ii) Discuss briefly phyletic lineage in biological organization.
ANSWER:
Phyletic Lineage:
When we look at the biodiversity (the number and variety of species in a place), we find that there are nearly 2,500,000 species of organisms, currently known to science. More than half of these are insects (53.1%) and another 17.6 % are vascular plants. Animals other than insects are 19.9 % (species) and 9.4 % are fungi, algae, protozoa, and various prokaryotes. This list is far from being complete. Various careful estimates put the total number of species between 5 and 30 million. Out of these only 2.5 million species have been identified so far. The life today has come into existence through Phyletic lineages or evolving populations of the organisms living in the remote past. Evolutionary change often produces new species and then increases biodiversity.
“A phyletic lineage is an unbroken series of species arranged in ancestor to descendant sequence with each later species having evolved from one that immediately proceeded it.”
If we had a complete record of the history of life on this planet, every lineage would extend back in time to the common origin of all early life. We lack that record because many soft bodied organisms of the past had not left their preserved record as fossils.
(iii) Write notes on the following:
(a) Living world in space and time
(b) Population
(c) Community
ANSWER:
(a) LIVING WORLD IN SPACE
Living world of today is enormous in size. It has been reproducing and evolving since the time of its origin on this planet. Today almost all parts of the world abounds in living organisms. The distribution of organisms in space can be studied through biomes. A biome is a large regional community primarily determined by climate. It has been found that the major type of plant determines the other kind of plants and animals. These biomes have, therefore, been named after the type of major plants or major feature of the ecosystem. The major biomes of the world you will study in the chapter of ecology.
(b) LIVING WORLD IN SPACE
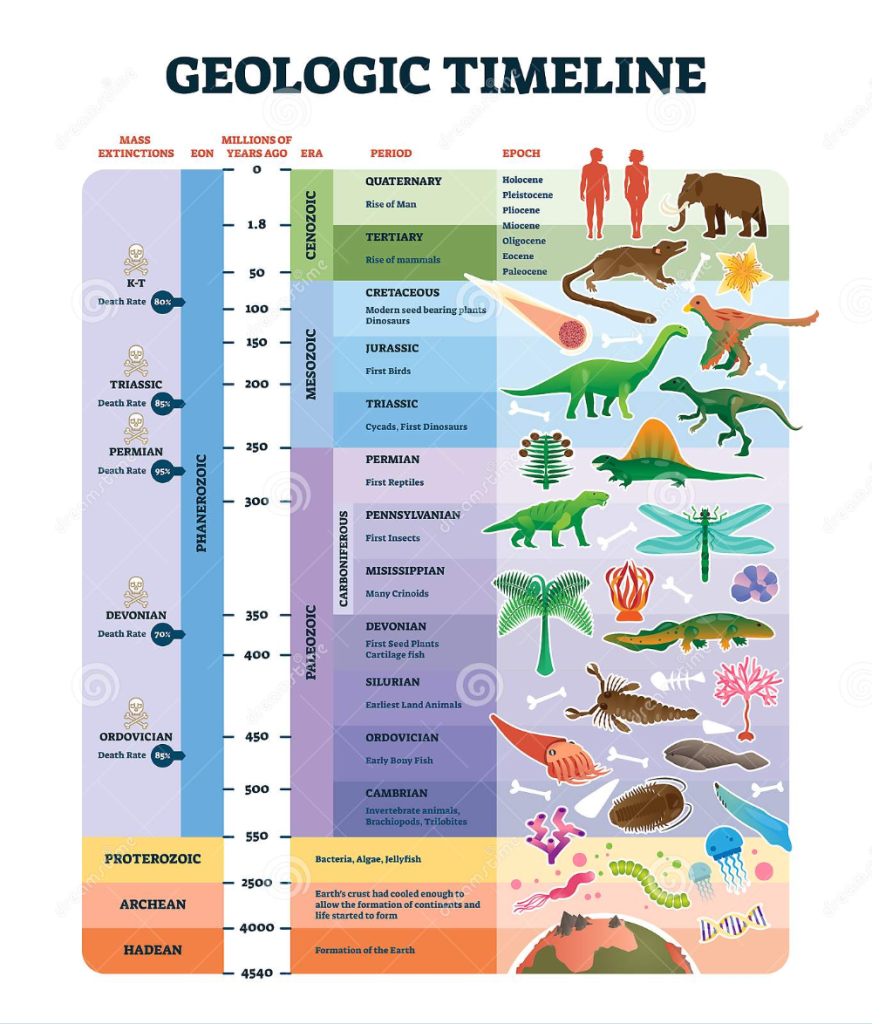
Since the time of origin of life on this planet, various organisms were evolved and dominated this planet during various periods of geological time chart. This has been found by the evidence obtained from the discovery and study of fossils which allows biologists to place organisms in a time sequence. As geological time passes and new layers of sediments are laid down, the older organisms should be in deeper layer, provided the sequence of the layers has not been disturbed. In addition, it is possible to date/age rocks by comparing the amounts of certain radioactive isotopes they contain. The older sediment layers have less of these specific radioactive isotopes than the younger layers. A comparison of the layers gives an indication of the relative age of the fossils found in the rocks. Therefore, the fossils found in the same layer must have been alive during the same geological period. You can have an idea about the temporal distribution of various forms of life both plants and animals in the various geological periods.
(b) POPULATION
“A population is a group of living organisms of the same species located in the same place at the same time.”
Examples are the number of rats in a field of rice, the number of students in your biology class, or human population in a city.
Population is a higher level of biological organization than organism (whole) because here a group of organisms of the same species is involved. This level of organization has its own attributes which come into being by living together of a group of organisms of the same species. Some of these attributes are gene frequency, gene low, age distribution, population density, population pressure etc. All these are new parameters which have appeared due to population of an organism.
(c) COMMUNITY
“Populations of different species (plants and animals) living in the same habitat form a community.”
Communities are dynamic collections of organisms, in which one population may increase and others may decrease due to fluctuation in abiotic factors. Some communities are complex and well interrelated, other communities may be simple. In a simple community, any change can have drastic and long lasting effects.
The organisms, interaction can take many shapes. It may be predation, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism and competition.
(iv) Explain the biological method for solving a biological problem. How do deductive and inductive reasoning play an important role in it?
ANSWER:
Consult textbook at page 9 —10.
(v) What is the role of the study of Biology in the welfare of mankind?
ANSWER:
Consult textbook at page 9 —10.
NOTE: Give your opinion about our work. ask if something more is required in the context of this chapter. Stay attached with our platform. Thanks!

