EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES IN CHEMISTRY
Q.01: Select the most suitable answers from the given ones in each question:
(i) A filtration process could be very time consuming if it were not aided by a gentle suction which is developed:
(a) If the paper covers the funnel up to its circumference.
(b) If the paper has got small sized pores in it.
(c) If the stem of the funnel is large so that it dips into the filtrate.
(d) If the paper fits tightly.
Ans: (d)
EXPLANATION: If the filter paper fits tightly along the walls of the funnel, there will be no air bubbles formed to break the column in funnel stem, the long continuous column of the filtrate in funnel stem exerts full suction on the solution across above filter paper, and thus the rate of filtration is increased.
(ii) During the process of crystallization, the hot saturated solution:
(a) Is cooled very slowly to get large sized crystals.
(b) Is cooled at a moderate rate to get medium sized crystals.
(c) Is evaporated to get the crystals of the product.
(d) Is mixed with an immiscible liquid to get the pure crystals of the product.
Ans: (b)
EXPLANATION: Moderate cooling is preferred over slow or rapid cooling because slow cooling yields bigger crystals which are likely to include considerable amount of solvent carrying impurities with it. Similarly, rapid cooling also results in the formation of smaller or less well-defined crystals because solute particles don’t have sufficient time to arrange properly.
(iii) Solvent extraction is an equilibrium process and is controlled by:
(a) Law of mass action
(b) The amount of solvent used
(c) Distribution law
(d) The amount of solute
Ans: (c)
EXPLANATION: In solvent extraction, a solute can be separated from a solution by shaking the solution with a solvent in which the solute is more soluble and the added solvent does not mix with the solution. Solvent extraction is controlled by ‘Distribution Law’ or ‘Partition Law’ which states that ‘a solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids in a constant ratio of concentrations irrespective of the amount of solute added.’
(iv) Solvent extraction method is a partially useful technique for separation when the product to be separated is:
(a) Non-volatile or thermally unstable
(b) Volatile or thermally stable
(c) Non-volatile or thermally stable
(d) Volatile or thermally unstable
Ans: (d)
EXPLANATION: Solvent extraction technique is used for the separation of the product which is volatile or thermally unstable because in this technique, the mixture need to be separated is not heated either to make saturated solution as in crystallization or in dry state like sublimation. so, most organic compounds which are often volatile and low boiling substances are separated by this technique.
(v) The comparative rates at which the solutes move in paper chromatography depend on:
(a) The size of paper
(b) Rf values of solutes
(c) Temperature of the experiment
(d) Size of the chromatographic tank used
Ans: (b)
EXPLANATION: The comparative rates at which the solutes move in paper chromatography depend on the Rf values of the solutes because Rf or retardation factor reflects the affinity of a component for stationary or moving phase used in chromatography. So, the component with smaller Rf value will cover smaller distance from original spot due to its affinity with stationary phase, while the component with greater Rf value will cover greater distance due to its more affinity with moving phase.
Q.02: Fill in the blanks:
(i) A complete chemical characterization of a compound must include _________. (Both qualitative and quantitative analyses)
(ii) During filtration the tip of the stem of the funnel should touch the side of the beaker to avoid ___________. (splashing)
(iii) A fluted filter paper is used to ___________ the process of filtration. (Speed up)
(iv) A solvent used for crystallization is required to dissolve __________ of the substance at its boiling point and __________ at the room temperature. (Large amount, small amount)
(v) Repeated solvent extractions using small portions of solvent are ____________ than using a single extraction with larger volume of the solvent. (More efficient)
Q.03: Tick the correct sentences. If the sentence is incorrect, write the correct statements.
(i) A qualitative analysis involves the identification of elements present in a compound.
(True)
(ii) If the process of filtration is to run smoothly, the stem of the funnel should remain empty.
(False)
Correct: If the process of filtration is to run smoothly, the stem of the funnel should remain full of liquid as well as there is a liquid in conical portion of the funnel.
(iii) If none of the solvents is found suitable for crystallization, a combination of two or more immiscible solvents may be used.
(False)
Correct: If none of the solvents is found suitable for crystallization, A combination of two or more miscible solvents may be used.
(iv) A solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids in a constant ratio of concentrations depending upon the amount of solvent added.
(False)
Correct: A solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids in a constant ratio of concentrations independent of the amount of solvent added.
(v) Paper chromatography is a technique of partition chromatography.
(True)
Q.04: Why is there a need to crystallize the crude product?
The crude product is needed to be crystallized to obtain the pure sample of the desired substance, so that it can be analyzed accurately, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Q.05: A water insoluble organic compound aspirin is prepared by the reaction of salicylic acid with a mixture of acetic acid and acetic anhydride. How will you separate the product from the reaction mixture?
Since, aspirin is insoluble in water, so it can be separated by filtration (vacuum filtration) using a filter paper in funnel. But there is some problem. Salicylic acid is also insoluble in water. If some amount of it remains unreacted, it will contaminate the aspirin crystals. Salicylic acid impurity is then checked by FeCl3 solution, and removed by recrystallization of aspirin.
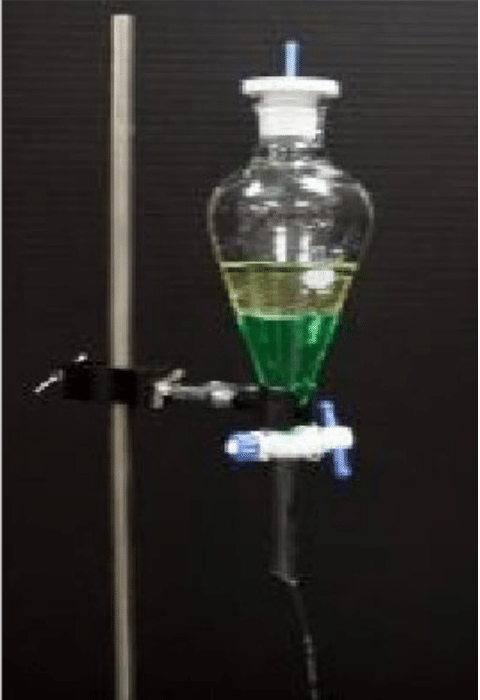
Q.06: A solid organic compound is soluble in water as well as in chloroform. During its preparation, it remains in aqueous layer. Describe a method to obtain from this layer.
An organic compound which is soluble in water as well as in chloroform, can be separated by solvent extraction. In this technique, the solution containing organic compound is shaken with chloroform in a separating funnel. The chloroform dissolves the organic compound more than water. So, most of the organic compound goes into chloroform layer, which is then separated and evaporated to get pure organic compound.

Q.07: The following figure shows a developed chromatogram on paper with five spots:
- Unknown mixture X
- Sample A
- Sample B
- Sample C
- Sample D
Find out:
(i) The composition of unknown mixture X
(ii) Which sample is impure and what is its composition.

Ans:
(i) The unknown mixture X is composed of B and C.
(ii) Sample D is impure. It is composed of A and C.

Q.08: In solvent extraction technique, why repeated extraction using small portions of solvent are more efficient than using a single extraction but larger volume of solvent?
Repeated extractions, using small quantities of solvent give greater amount of solute than using a large amount of the solvent in a single extraction. This is because the solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids in a constant ratio of concentration, irrespective of the amount of the solute. Thus, when small quantities of second solvent are used repeatedly, greater proportion of solute can be separated.
Q.09: Write down the main characteristics of a solvent selected for crystallization of a compound.
The solvent chosen for crystallization should have the following characteristics:
- It should dissolve a large amount of the solute at its boiling point and only a small amount at room temperature.
- It should not react chemically with the solute.
- It should not dissolve the impurities.
- It should deposit well–formed crystals on cooling.
- It should be inexpensive.
- It should be safe to use and easy to remove.
Q.10: You have been provided with a mixture containing three inks with different colours. Write down the procedure to separate the mixture with the help of paper chromatography
Ans:
Separation of Inks from Ink mixture by Paper Chromatography:
Paper chromatography is a technique of partition chromatography. This can be used to separate inks from an ink mixture. For this purpose, first take a chromatographic tank. Pour a specially prepared solvent mixture, in accordance with the sample to be separated, into this chromatographic tank. Cover the tank to homogenize its inner atmosphere. Take about 20cm strip of Whatmann’s chromatographic paper No.1. Draw on it a thin pencil line about 2.5 cm from one end. Spot a point, on the pencil line, with the mixture of inks. Add three sample spots of pure inks along the mixture spot for identification. When the spots have dried, suspend the paper with clips so that the impregnated end dips into solvent mixture to a depth of 5–6 mm. Cover the tank. As the solvent front passes the spots, the inks begin to move upward.
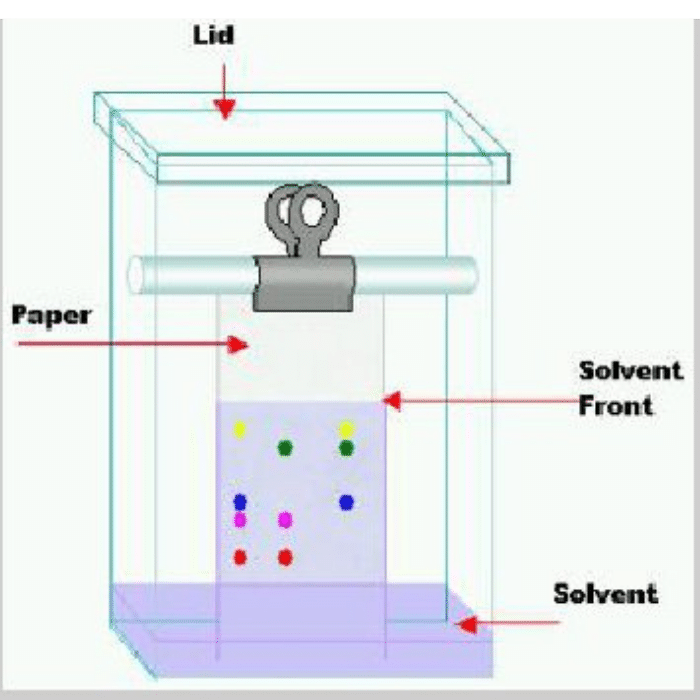
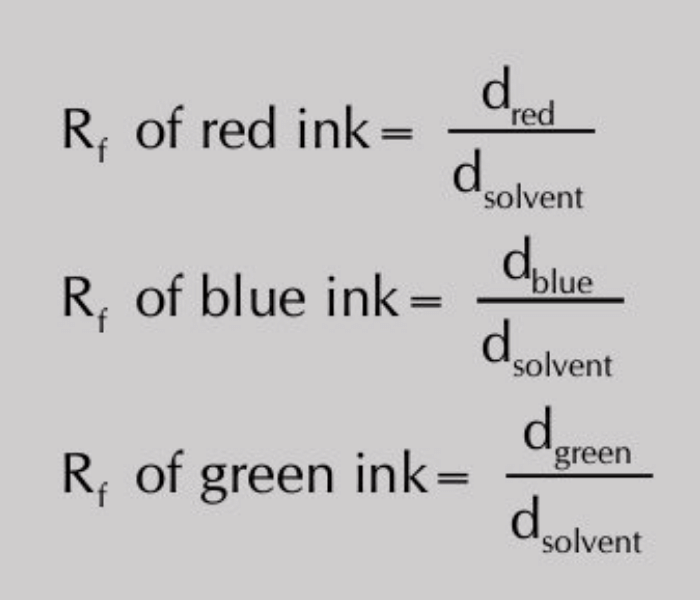
The rate at which they move depends on their distribution coefficients. When the solvent front has risen to about 3/4 the of the length of the paper, remove the strip, mark the solvent front with a pencil and allow the strip to dry. Once the paper is dried, the pattern of different inks on the paper is called a chromatogram. Each colour has a specific retardation factor called Rf value. The Rf value is related to its distribution coefficient and is given by:

Then Rf value of each ink will be calculated as: